Basic Deployment Automation
Small SaaS Provider: Established a foundational Continuous Delivery (CD) workflow using Jenkins to accelerate the release cycle of their core software updates to a cloud server.
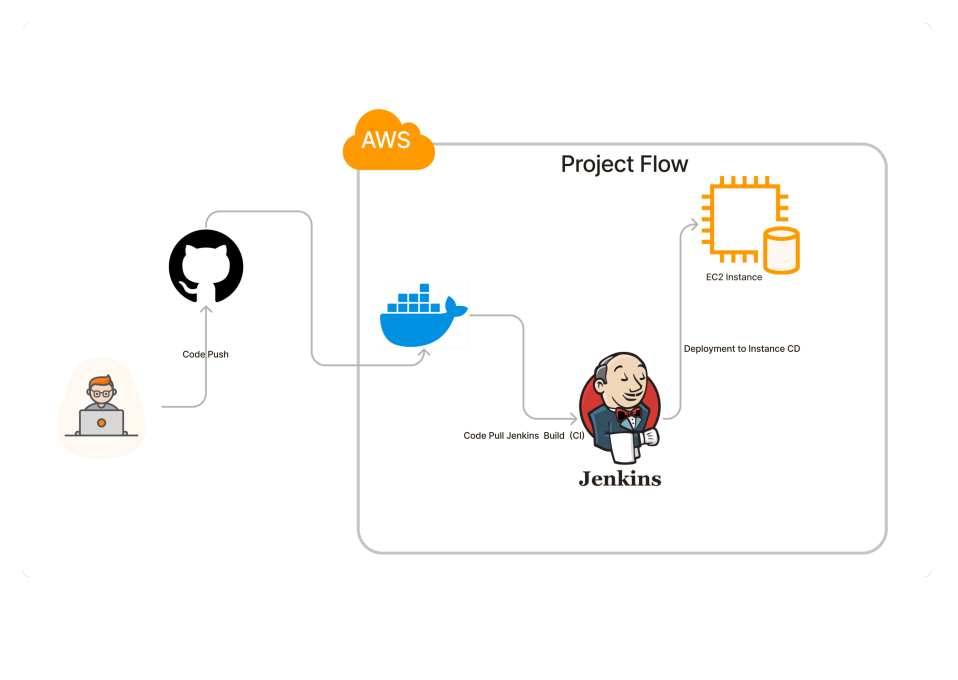
This diagram illustrates a fundamental Continuous Integration (CI) and Continuous Delivery (CD) pipeline that we implemented for the project. Here is a breakdown of the process and the technologies used, designed to highlight its efficiency and automation for your customers:
Pipeline Workflow and Automation
We established an automated pipeline using industry-standard tools to rapidly and reliably take code changes from a developer's machine all the way to a running application in the cloud. This approach maximizes development speed while minimizing the risk of errors during deployment.
1. Code Commit & Push:
- A developer writes code and performs a "Code Push" to the central version control system, GitHub.
- Value: All code changes are tracked, auditable, and stored securely, enabling collaboration and easy rollbacks.
2. Continuous Integration (CI) & Build:
- Jenkins (Our Automation Server) automatically detects the new code push on GitHub (Code Pull).
- Jenkins then initiates the "Build (CI)"process. This includes compiling the code, running tests, and crucially, creating a Docker container image of the application. * Value: This step immediately validates the code, catching integration and build errors early. Docker ensures the application runs consistently across all environments, eliminating "it worked on my machine" issues.
3. Deployment (Continuous Delivery - CD):
- Once the Docker image is built, Jenkins proceeds with the "Deployment to Instance (CD)" phase.
- The application (as a Docker container) is deployed to the target EC2 Instance (a virtual server on AWS).
- Value: This process is fully automated, repeatable, and fast, allowing us to deploy new features and bug fixes to the production environment (or any environment) quickly and confidently.
Key Technologies Used
| Technology | Role in the Project | Value to the Customer |
|---|---|---|
| GitHub | Source Code Management (SCM) | Secure, collaborative platform for storing and versioning the application code. |
| Jenkins | Automation Server / CI/CD Engine | Orchestrates the entire automated process, from code pull to application deployment. |
| Docker | Containerization | Packages the application and all dependencies into a portable container for consistent deployments. |
| AWS EC2 | Cloud Compute Infrastructure | Provides reliable, scalable cloud servers to run the application. |
Why This Pipeline Is A Competitive Advantage
- Reliability: Every deployment follows the exact same automated steps, resulting in fewer human errors.
- Speed: New features can be delivered to end-users faster than traditional manual processes.
- Consistency: Docker containers ensure the application behaves identically in development, testing, and production environments.
- Cost Efficiency: Automation reduces manual effort and associated costs, allowing the team to focus on development rather than deployment tasks.
This solution gives the customer a modern, agile foundation capable of supporting continuous product evolution.